What is a Busway? Definition and Classification of Busway Systems
A busway, also known as a busbar trunking system, is a modern, efficient, and energy-saving solution for power distribution. It is widely used in commercial buildings, industrial plants, and high-rise facilities.
A busway consists of copper or aluminum conductors, which are supported by non-combustible insulating materials and enclosed in a protective metal housing. This design ensures safety, reliability, and durability in demanding electrical environments.
Advantages Over Traditional Conduit Systems
Compared to conventional conduit wiring systems, busways offer:
Greater flexibility in design and layout
Simplified installation and future expansion
Improved aesthetics for modern buildings
Reduced maintenance and operational costs
These benefits have made busways a preferred choice for large-scale and complex electrical infrastructure projects.
What You’ll Learn
In this article, we will explore:
The different types of busways and their applications
How to select the right busway for your project
Key factors electrical designers should consider
Whether you’re designing a factory, commercial center, or high-rise building, this guide will help you make informed decisions about busway systems.
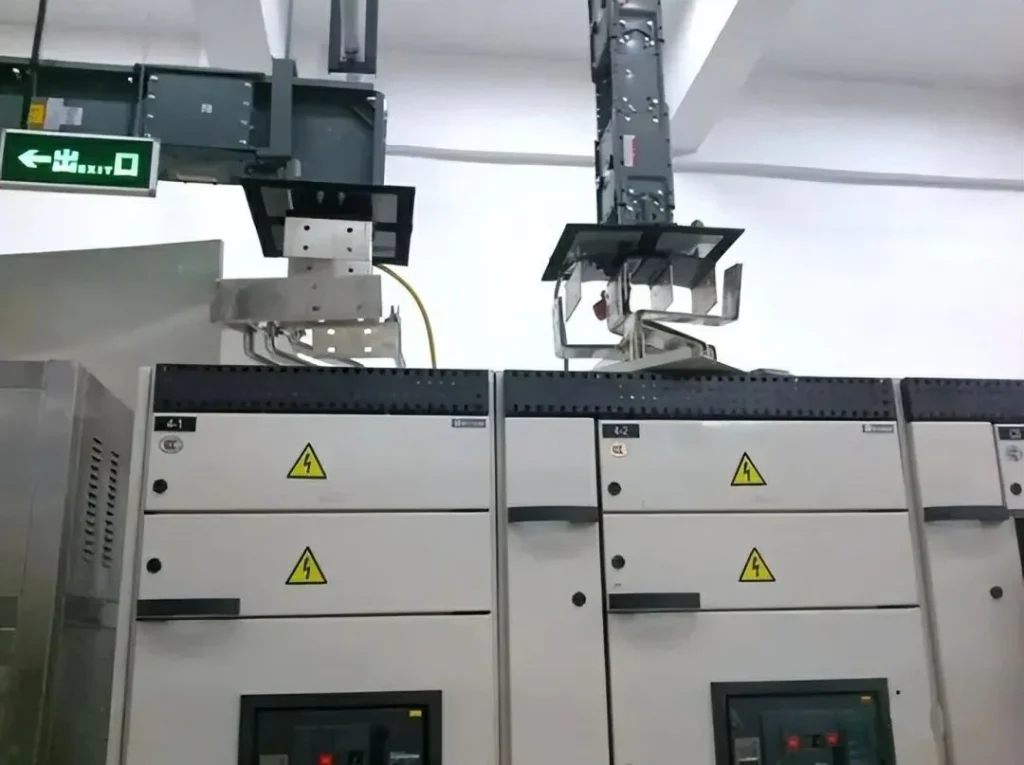

Definition and Classification of Busways
What is a Busway?
In low-voltage electrical distribution design, a busway is a critical component of the distribution trunk system. According to the Chinese national standard GB7251.6-2015 “Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies—Part 6: Busbar trunking systems (Busways),” a busway is defined as:
Busway: An enclosed assembly formed by a conductor system, used for power distribution and control for all types of loads. It is suitable for industrial, commercial, and similar applications. The conductor system is enclosed in a duct, trunking, or similar casing, with busbars insulated and supported by insulating materials.
Types of Busways
Busways can be classified based on their structure or usage environment:
By Structure:
- Air Insulated Busways: The busbars are insulated by air and protected by a metal casing. Due to its reliance on air convection for cooling, this type of busway is less efficient at heat dissipation and is thus more suitable for low-current applications.

- Compact Insulated Busways: The busbars are wrapped with solid insulation materials and tightly enclosed in a metal casing. Compact busways are more efficient at conducting heat and are ideal for high-current applications.
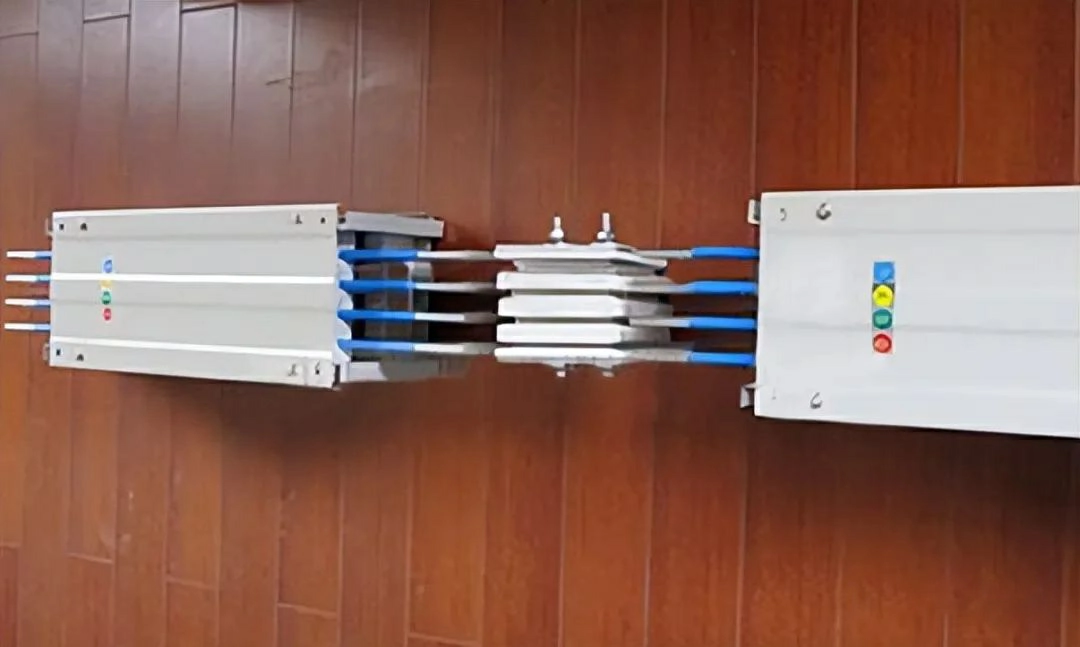
By Usage Environment:
- Standard Busways: Non-fire-resistant and non-flame-retardant busway, used in ordinary electrical loads. In the event of a short circuit, it can pose a fire risk as the flames may spread through connected busways.
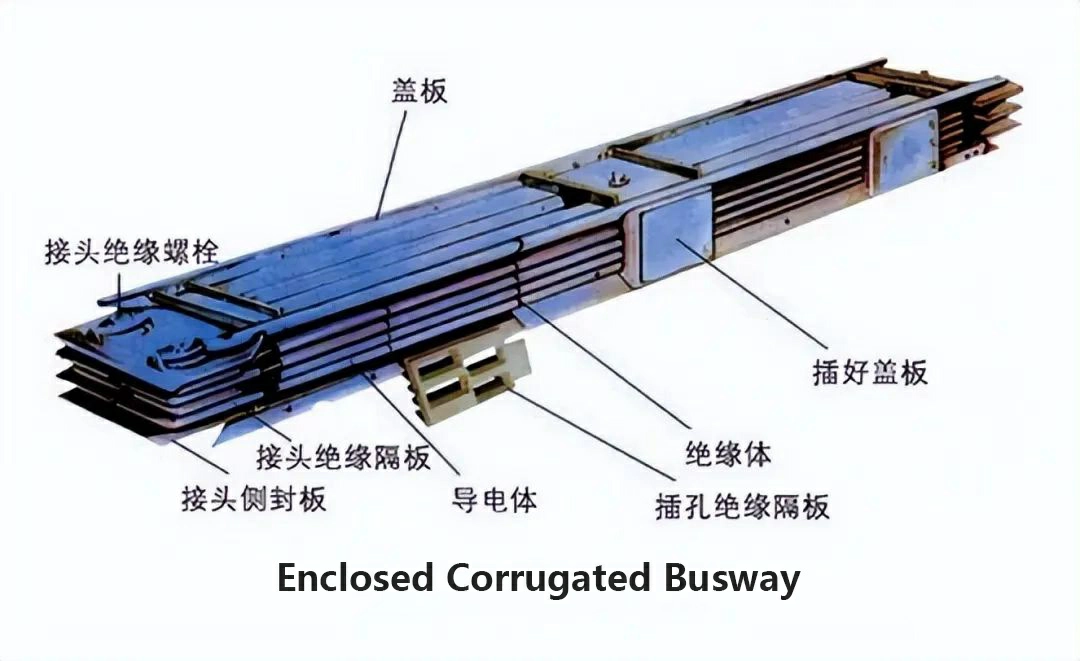
- Flame-Retardant Busway: The flame does not spread to other sections of the busways during a fire, as both the metal casing and insulating materials are flame-retardant.
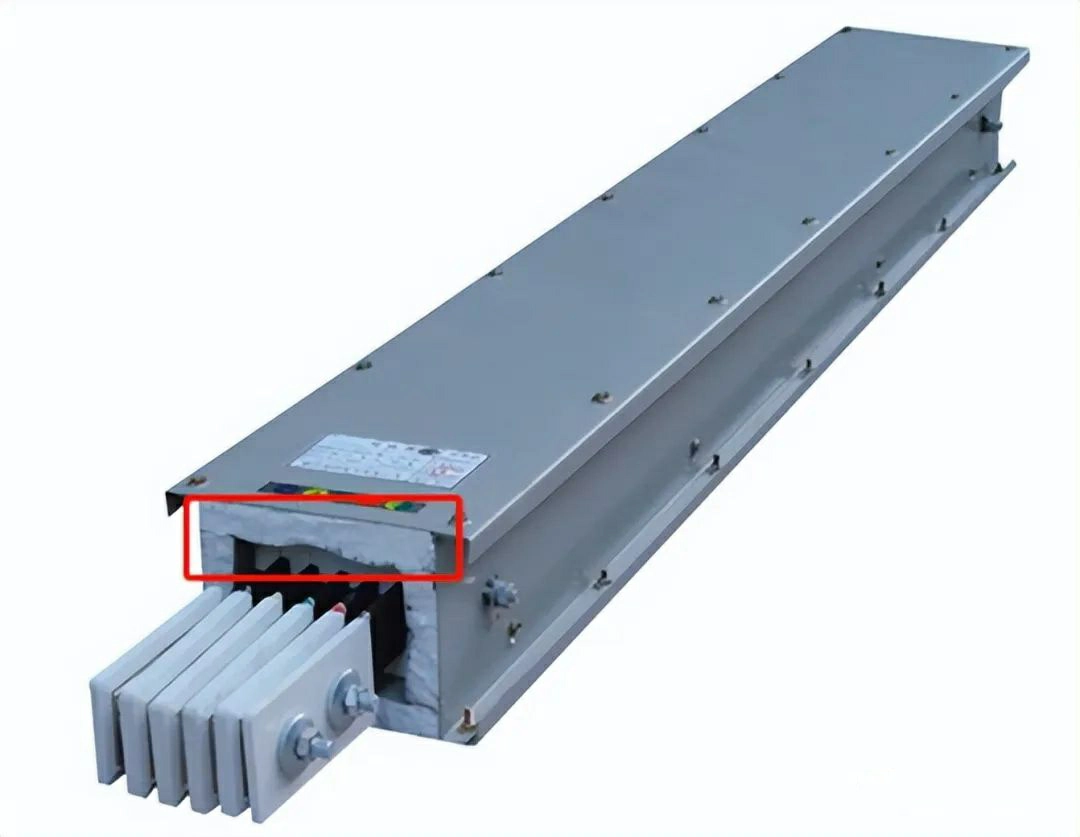
- Fire-Resistant Busway: Maintains circuit integrity for a specified period under fire conditions. Fire-resistant busways are insulated with fireproof or flame-retardant materials and must pass the type tests defined in JB/T10327-2011 “Fire-Resistant Busbar Trunking Systems” to ensure their performance in fire scenarios.
Key Considerations for Busway Selection
When selecting a busway, several factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance:
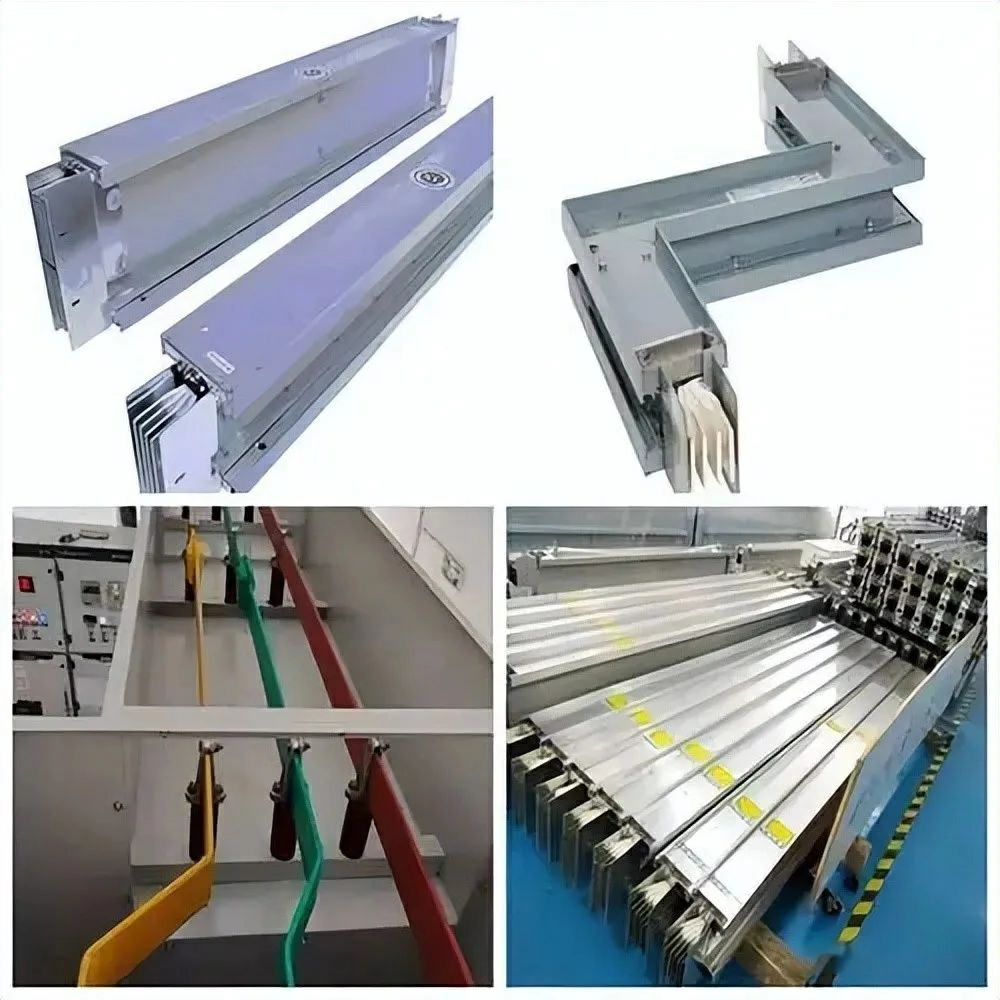

How to Select Busway Based on Installation Location
Choosing the right busway depends heavily on the installation environment. Each location has different safety, durability, and protection requirements.
1. Indoor Environments
For specialized indoor settings (e.g., high-capacity substations), use busways with a protection rating of IP30. This allows better heat dissipation in controlled environments.
For standard indoor applications (e.g., distribution rooms, electrical shafts), choose busways with at least IP40 protection. This ensures basic safety and protection against solid objects and accidental contact.
2. Humid or Splash-Prone Areas
In areas exposed to moisture or occasional splashes, select busways rated IP54 or higher. This rating protects against dust and water spray, ensuring stable and reliable operation in damp environments.
3. Outdoor and Corrosive Environments
- For outdoor or corrosive locations (e.g., coastal areas with salt spray or industrial zones with chemical exposure), use resin-insulated busways or reinforced casing designs.
- These options provide maximum durability and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term performance in harsh conditions.
How to Select Busway Based on Current Rating
Selecting the correct rated current (IN) ensures both safety and cost efficiency.
1. Base It on Operational Current (IB)
The rated current should be slightly higher than the actual operational current (IB) to ensure continuous, safe operation without overheating.
2. Consider Product Specifications
Take into account the busway’s:
Heat dissipation performance
Internal impedance
Energy loss
Material cost
3. Popular Choice: Aluminum Alloy Low-Impedance Compact Busways
These busways are widely used due to:
Excellent thermal performance
Low power loss
Cost-effective construction
4. Follow Manufacturer Standards
Always choose a busway that conforms to the manufacturer’s official specifications. This ensures compatibility, performance, and warranty compliance.
By considering these factors, you can choose the most suitable busway for your specific needs, ensuring both safety and efficiency in your electrical distribution system.
Table of Contents
Have you Any Questions?
Can’t find an answer to your question, or want more information about our products? If so, please feel free to get in touch with our professional team. We’re here to help you drive your projects to success.
