What Are Grid-Tied, Off-Grid, Hybrid, and Microgrid Photovoltaic Systems?
With the increasing global demand for renewable energy, photovoltaic (PV) power generation has become one of the most important green energy sources. As a flexible and efficient energy solution, distributed PV systems are being increasingly deployed in homes, commercial buildings, and industrial facilities. There are several common operating modes for distributed PV systems, including grid-tied, off-grid, hybrid, and microgrid systems. Understanding these concepts is crucial for selecting the right PV system for your needs. In this article, we will explain the meaning of these modes and explore their differences, advantages, and practical applications.
What is a Grid-Tied Photovoltaic System?
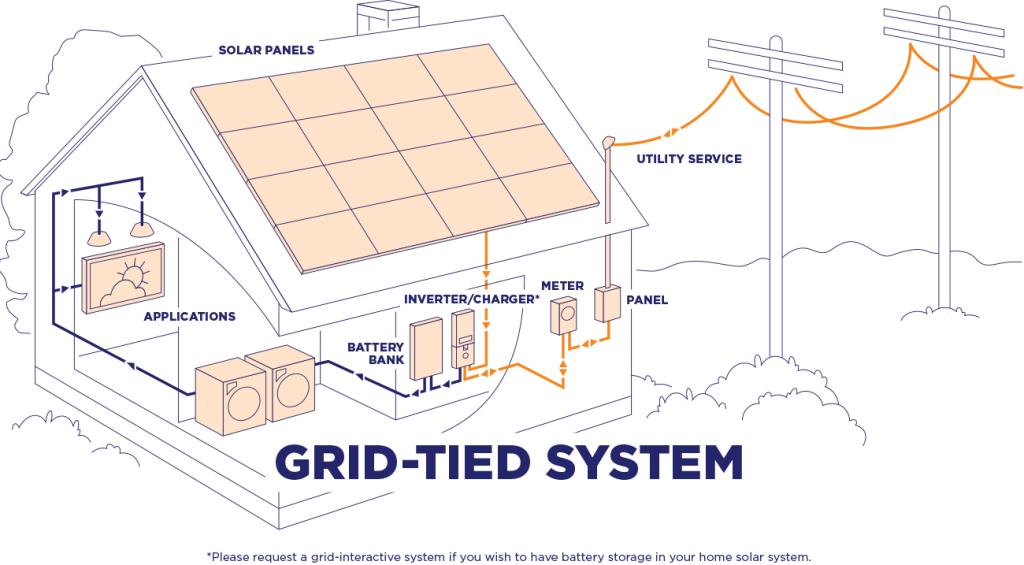
A grid-tied PV system is one that connects a solar power system to the public electrical grid, allowing for two-way electricity flow. During the day, the PV panels generate power; part of the energy is used to meet the system’s own demand, and the excess is sent to the grid through an inverter for use by other consumers. If the PV system’s energy output is insufficient to meet the user’s needs, the user can draw supplemental power from the grid.
Advantages of Grid-Tied Systems:
- Reduced Electricity Costs: Users can sell excess electricity back to the grid, lowering their electricity bills.
- High Stability: The grid ensures a stable electricity supply, preventing power shortages.
- Policy Support: Many governments offer subsidies, feed-in tariffs, or tax incentives for grid-tied PV systems.
Application Scenarios of Grid-Tied Systems:
Grid-tied PV systems are most commonly used in residential homes, commercial buildings, and industrial parks in urban areas, where the grid infrastructure is already well-established.
What is an Off-Grid Photovoltaic System?
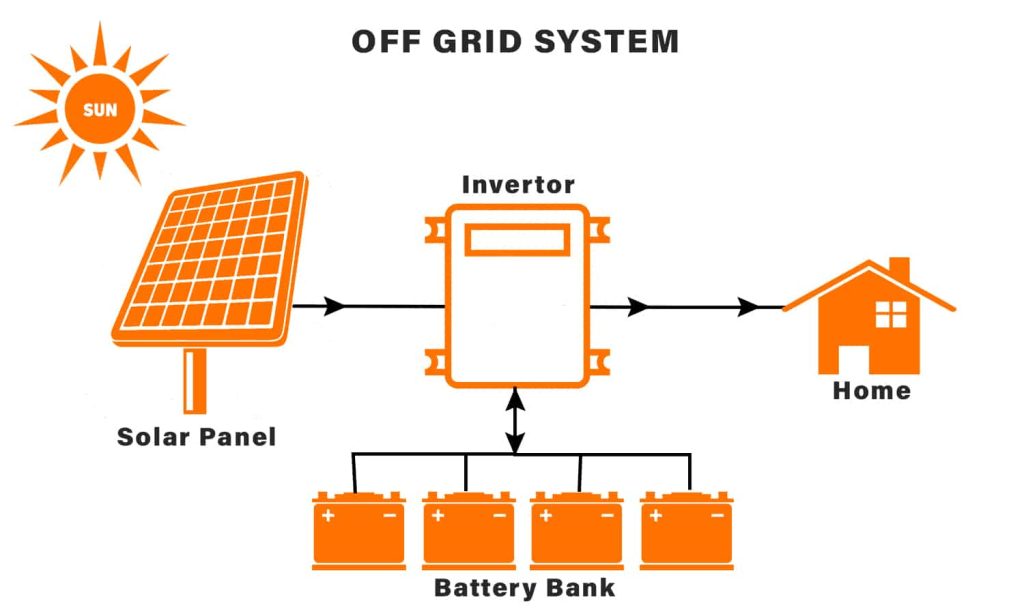
An off-grid PV system operates independently of the electrical grid. This system usually includes solar panels, batteries, and an inverter to directly supply electricity to the user or store excess energy for later use. Off-grid systems are especially suitable for remote locations or special circumstances where access to the electrical grid is unavailable.
Advantages of Off-Grid Systems:
- Independence: Users are not reliant on the public grid and have full control over their energy consumption.
- Ideal for Remote Areas: In locations far from the grid, off-grid systems can provide a reliable power supply.
- Reduced Grid Dependence: Off-grid systems reduce reliance on the grid, enhancing energy security, especially in case of grid failure.
Application Scenarios of Off-Grid Systems:
Off-grid PV systems are widely used in remote rural areas, islands, exploration bases, or any locations that lack grid infrastructure. They are also useful for disaster recovery or emergency power supply.
What is a Hybrid Photovoltaic System?
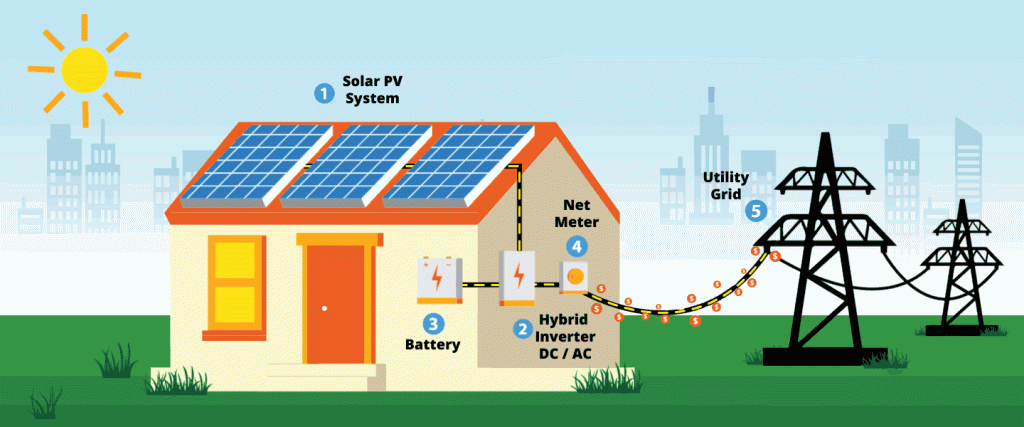
A hybrid PV system combines both grid-tied and off-grid capabilities, allowing the system to automatically switch between modes as needed. Under normal conditions, the system operates in grid-tied mode, sending excess power to the grid. However, if the grid experiences a power outage, the system can switch to off-grid mode and supply power from stored energy, ensuring an uninterrupted power supply.
Advantages of Hybrid Systems:
- Dual Protection: Combines the benefits of grid-tied and off-grid systems, ensuring reliability and stability.
- High Flexibility: The system can automatically switch between grid and off-grid modes based on power demand and grid conditions.
- Cost Savings: Users can take advantage of low electricity rates in grid-tied mode and switch to off-grid mode during outages, reducing the need for backup power.
Application Scenarios of Hybrid Systems:
Hybrid systems are suitable for locations that require both grid electricity and backup power during outages. They are ideal for industrial parks, hospitals, and shopping malls, where power stability is critical.
What is a Microgrid Photovoltaic System?
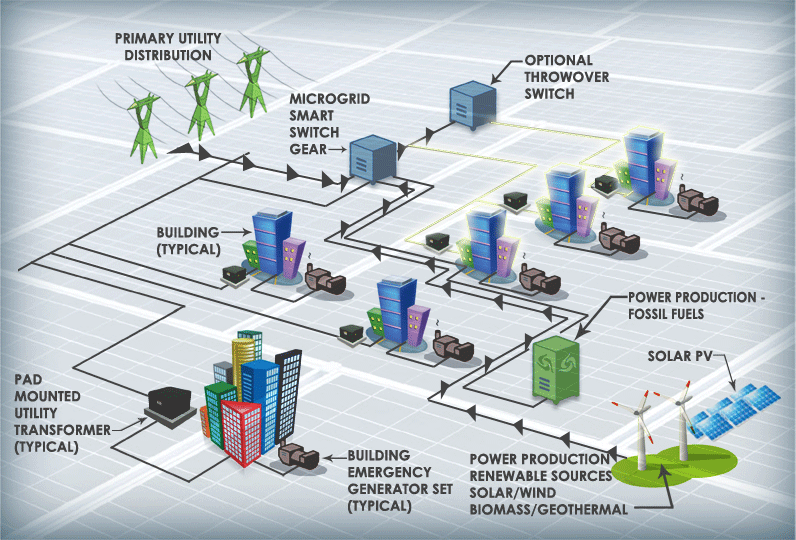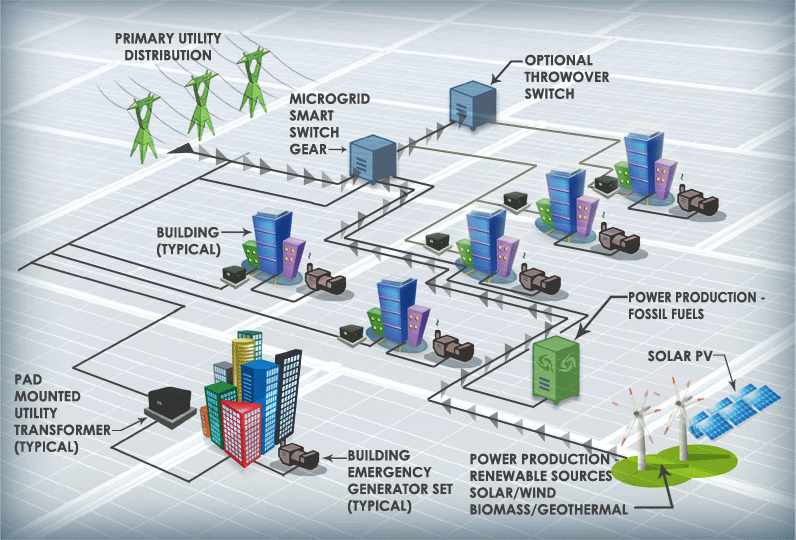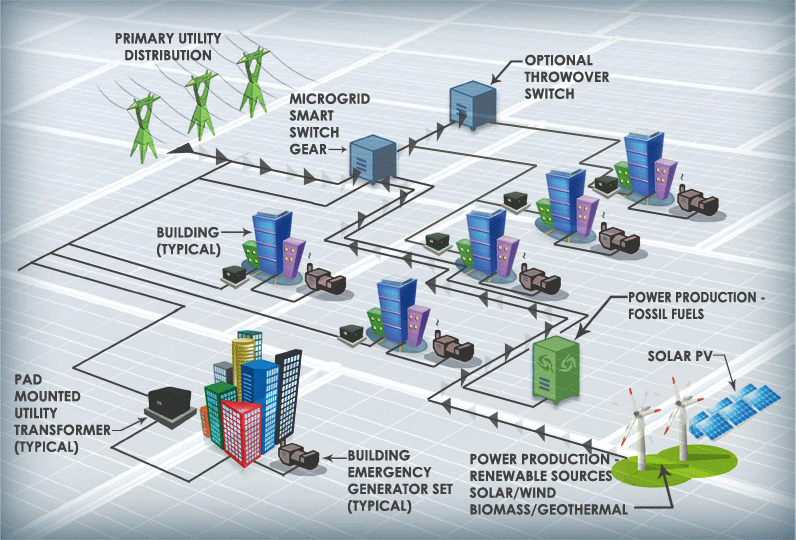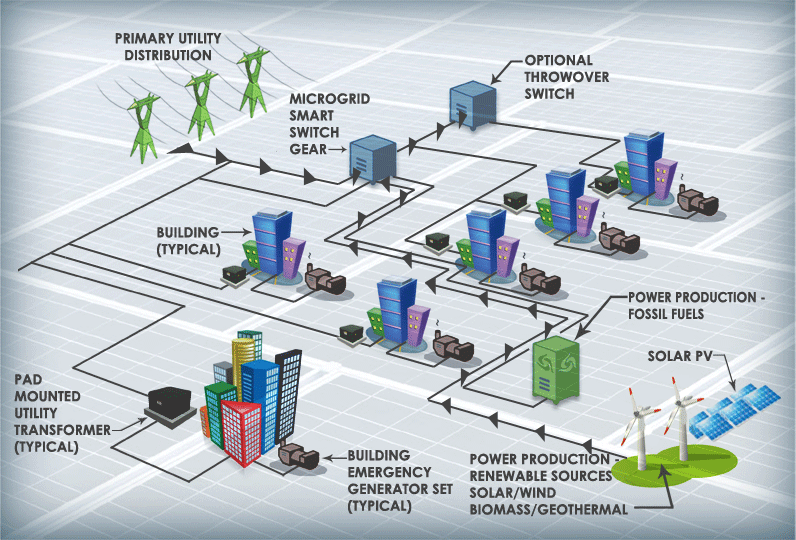
A microgrid PV System is a small-scale power grid that integrates multiple energy sources, such as PV power, wind energy, diesel generators, and more. It typically includes power generation, storage, and load management systems and can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. In a microgrid, a PV system can work with other renewable energy or traditional power sources to provide reliable power.
A microgrid can exchange electricity with the grid when connected, and in the event of a grid failure, it can operate autonomously, ensuring continuous power supply.
Advantages of Microgrids Systems:
- High Reliability: Microgrids can continue to provide electricity even during grid failures, increasing power reliability.
- Flexible Energy Management: By integrating multiple energy sources, microgrids can adjust energy supply according to demand.
- Supports Renewable Energy: Microgrids can make full use of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, reducing dependence on traditional fossil fuels and promoting green, low-carbon development.
Application Scenarios of Microgrids Systems:
Microgrids are ideal for large commercial facilities, industrial parks, military bases, hospitals, and schools that require high power reliability. Microgrids can also be used in remote areas as independent systems disconnected from the main grid.
Comparison of Grid-Tied, Off-Grid, Hybrid, and Microgrid Systems
| Feature | Grid-Tied PV System | Off-Grid PV System | Hybrid PV System | Microgrid PV System |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connection to the Grid | Always connected to the grid, two-way power flow | Completely independent of the grid | Connected to the grid but can switch to off-grid mode during power outages | Can connect to the grid or operate independently |
| Need for Storage | No storage needed (grid acts as storage) | Requires storage (e.g., batteries) | Requires storage for off-grid mode | Requires storage to ensure independence from the grid |
| Typical Applications | Urban areas, commercial and industrial zones | Remote areas, islands, emergency power | Remote areas, islands, emergency power | Industrial parks, hospitals, commercial facilities requiring high reliability |
| System Complexity & Cost | Simple system, low installation cost | Complex system, higher installation and maintenance costs | More complex system with higher costs due to switching mechanisms | Highly complex, integration of various energy sources, high costs |
| Power Reliability | Dependent on grid stability | Independent, but reliability depends on storage | High reliability, can switch between grid and off-grid | Very high reliability, can adapt to grid failures and integrate multiple energy sources |
Conclusion
When selecting a distributed photovoltaic (PV) system, understanding the differences between grid-tied, off-grid, hybrid, and microgrid systems is essential. Each system has its own advantages, making it suitable for different scenarios based on the location, energy needs, and desired level of independence. Whether you are looking to reduce electricity costs, ensure uninterrupted power supply during outages, or integrate renewable energy sources for sustainability, these PV system options offer flexible and efficient solutions for diverse energy requirements.
Have youAny Questions?
Can’t find an answer to your question, or want more information about our products? If so, please feel free to get in touch with our professional team. We’re here to help you drive your projects to success.

